I recently finished the Introduction to User Experience Design course on Coursera and here are my takeaways.
“ Design is a systematic and data driven process “
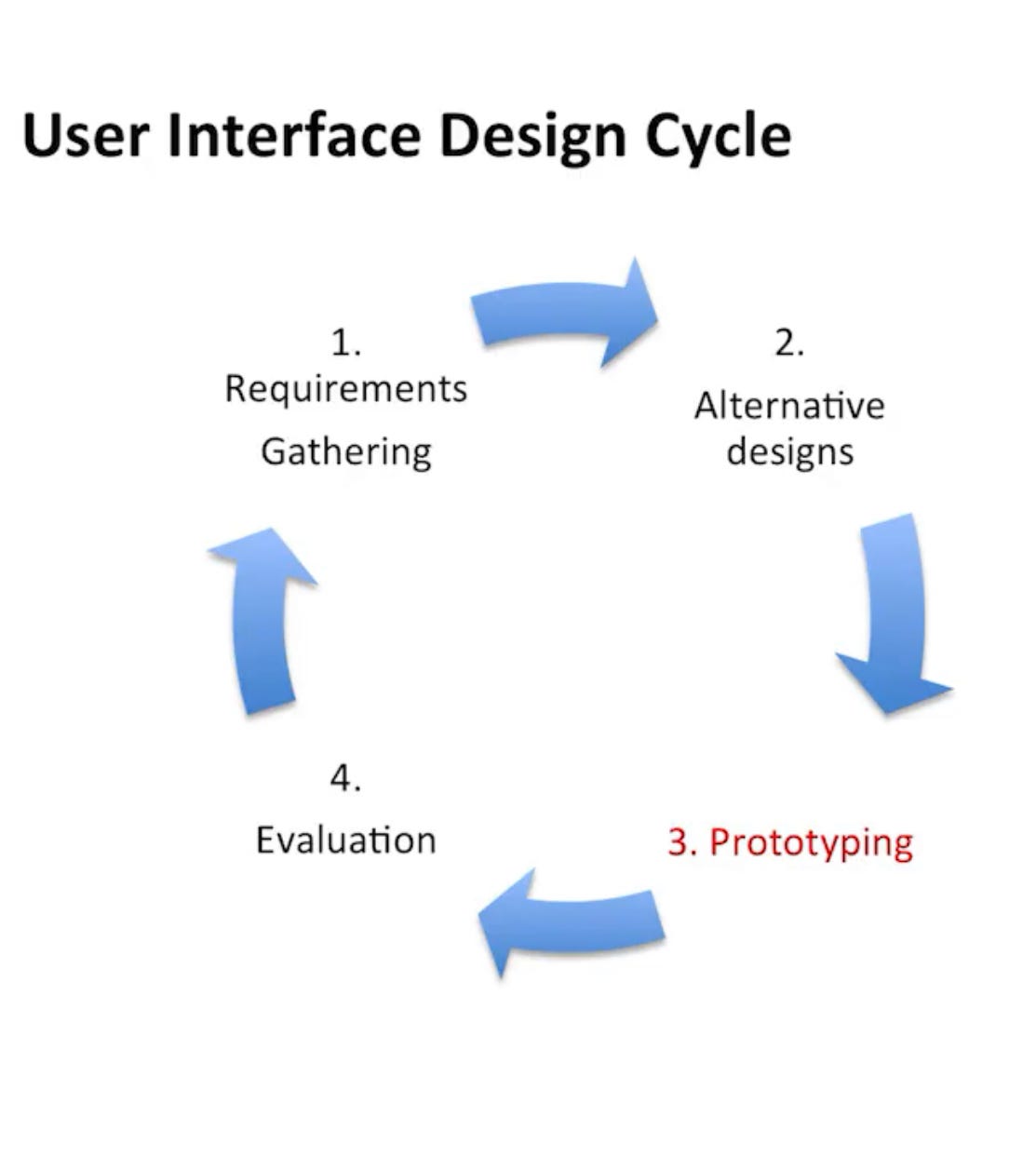
The UX design process is based on a set of techniques and also on a cycle of discovery:
Requirement Gathering is understanding the user and what their goals are. What are current practices. This step is where we can understand the “problem space” - what is hindering the completion of a certain task or process to be improved.
Scenarios : Build a narrative of how we currently complete the task
Hierarchical Task analyses : Create an outline of how the user is currently completing the task.
UI Critique : Take the UI for a spin and identify the task.
Objective Measure: How long it takes to complete a task.
There are four discovery techniques:
Naturalistic Observations: Takes place in the field with no interaction between the user and the designer.
Surveys: Get the user’s opinions through a set of questions.
Focus Groups: Takes place in a lab with a high degree of interaction.
Interviews: Get in depth information from the user.
Design Alternatives are once you understand the user, their goals, and their current practices you are able to take this data and develop various options that will improve the user experience. In this step, our job is to hone in on what problems we want to solve. This becomes our “design space”.
“Designing novel interfaces is all about finding improved ways to mediate how the user accomplishes a task.”
Our design must be useful and usable. By useful I mean to improve the user’s ability to complete the task and by usable I mean that our designs are grounded in the functional and non functional requirements observed in the previous step.
Important techniques used are brainstorming exercises and affinity diagrams.
Prototyping is a technique for modeling the “novel designs“ before a final version is produced. Here we will make sure that our designs actually meet the user’s needs. Prototyping is very important as it allows us to save time and money by creating models of our design without engaging with a highly trained professional, such as a software engineer.
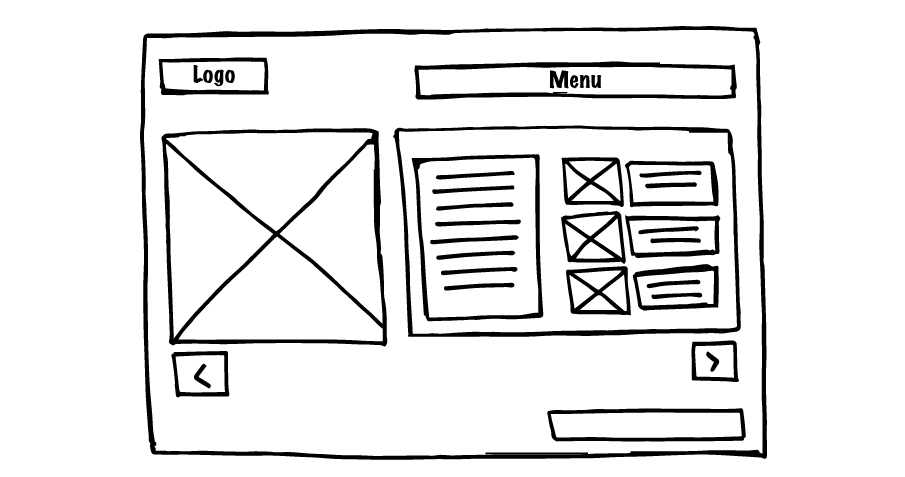
Low fidelity prototyping were aren’t going for perfection. We are looking for sequential iteration to improve a aspect of our design. Some examples of this are sketching (wire framing as seen below), story boarding and card-based prototypes.
Once our low fidelity prototypes can’t support our design objectives or we have learned all we can we switch to high fidelity prototypes. This is were we start using company resources to improve our prototypes and get closer to the final version of our design.
Some examples of high fidelity prototypes include:
The Wizard of Oz technique: Mimic the functionality of a product by having a human perform the task usually performed by a computer.
Proof of Concept video: Gives you a sense of how the system would work, showing various features and functionality.
Metaphor Development technique: Meant to help the user build a relevant mental model of how a design functions.
Evaluation is a set of techniques for ascertaining that your design meets the needs of the user. The goal of novel design is is to provide an improved user experience. Evaluation implies that you collect data. The type of data collected can be defined into two categories formative data and summative data. Formative data is gathered from your low fidelity prototypes and summative data from your high fidelity prototypes.
Other aspects we consider are learnability and memorability. Learnability refers to to how easy it is to complete the task successfully. We can get an objective measure by looking at time of completion or number of clicks compared to the experts. Memorability refers to how easy it is to remember how to use a product after repeated trials. We can measure the amount of time or number of clicks to complete a task over repeated trials to get a measure of memorability.
This sums up the important points learned throughout this introductory course. The course is divided up into 6 weeks and is completely free.(You just need to sign up to Coursera) I would definitely recommend it to learn the basics of UX design and also get comfortable with the terminology. Again, if you liked this type of post share it with someone who would benefit from it. If you have any questions feel free to reach out.
- Max